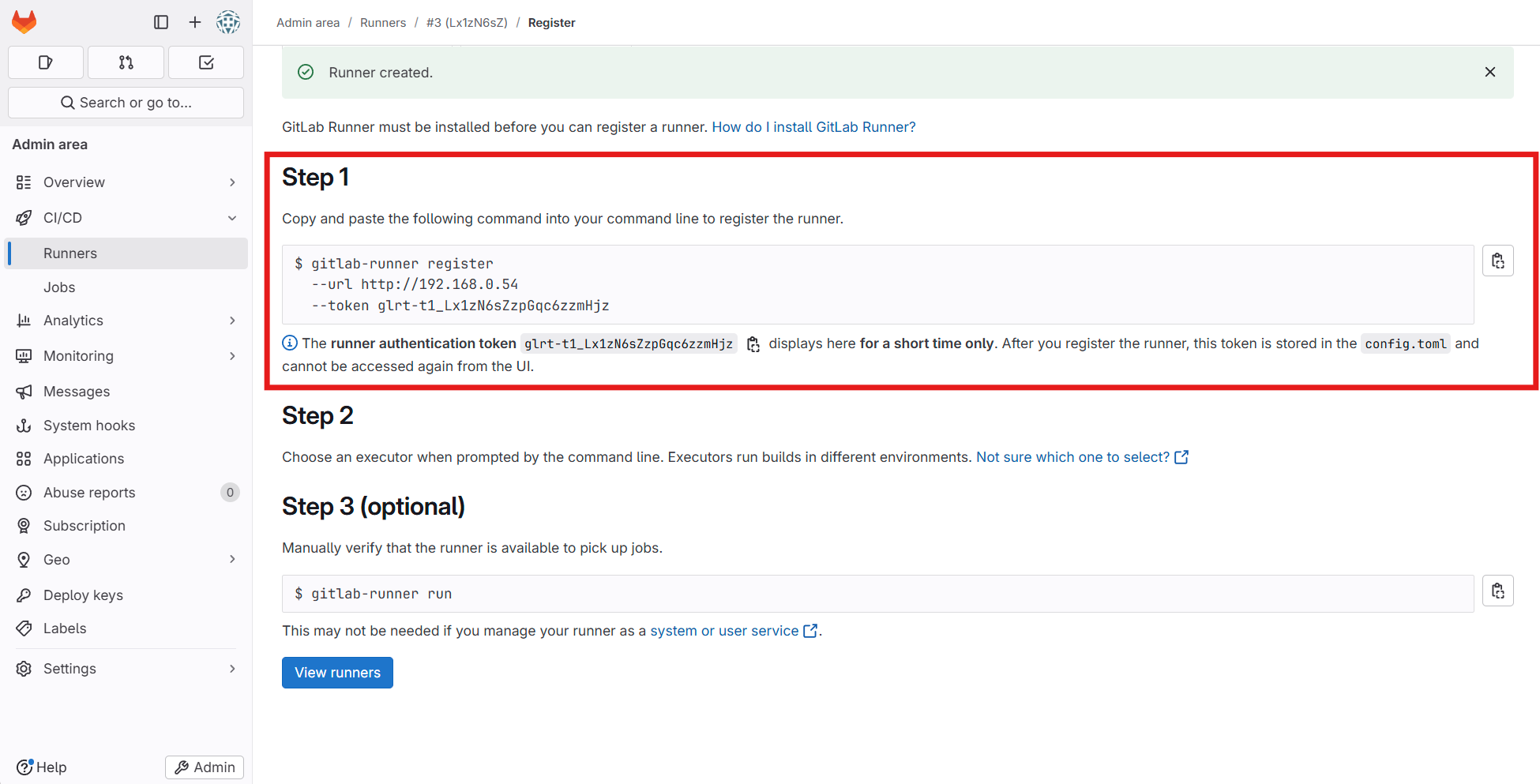
[Kubernetes] Install Gitlab Runner
[Kubernetes] Install Gitlab Runner
Helm Chart를 사용하여 GitLab Runner 설치
- GitLab Helm 리포지터리를 추가
1
helm repo add gitlab https://charts.gitlab.io
values.yaml파일을 사용하여 실행1
helm install --namespace <NAMESPACE> gitlab-runner -f <CONFIG_VALUES_FILE> gitlab/gitlab-runner
<NAMESPACE>는 GitLab 러너를 설치하기 원하는 Kubernetes Namespace<CONFIG_VALUES_FILE>은 커스텀 설정이 포함된 파일의 경로. Helm Chart를 사용
Values 작성
- gitlab과 연결을 위해 아래와 같이 설정
1 2
gitlabUrl: https://gitlab.com # gitlab url 입력 runnerRegistrationToken: a-trnA24KR77Mh***** # registration token 생성(CI/CD > Runner > New Project Runner)
만약 ci를 사용하여 image build를 하는 경우
- Docker In Docker (Dind) 혹은 buildah 같은 image를 사용하여 container 안에서 image를 생성해야 하는데 이 경우 gitlab-runner의 옵션을 추가해야 한다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
runners: config: | [[runners]] [runners.kubernetes] namespace = "{{.Release.Namespace}}" image = "ubuntu:20.04" privileged = true
- 기본 runner 설정은 ubuntu 이미지를 base로 사용하도록 되어있는데 이 부분에
privileged = true옵션을 추가해야 container 내부에서 image를 생성할 수 있는 권한이 추가된다.
RBAC 지원 활성화하기
ERROR: Job failed (system failure): secrets is forbidden- 만약 다음 에러가 발생한다면 RBAC 기능을 활성화해야 한다.
1 2
Using Kubernetes executor with image alpine ... ERROR: Job failed (system failure): secrets is forbidden: User "system:serviceaccount:gitlab:default" cannot create resource "secrets" in API group "" in the namespace "gitlab"
- 만약 클러스터가 RBAC를 사용하도록 설정한 경우, 차트가 자신의 서비스 계정을 만들거나 이미 만들어진 것을 사용하는 것을 선택할 수 있다.
- 차트에서 서비스 계정을 만들려면 rbac.create를 true로 설정
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
rbac: create: true rules: - resources: ["configmaps", "events", "pods", "pods/attach", "pods/exec", "secrets", "services"] verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "patch", "update", "delete"] - apiGroups: [""] resources: ["pods/exec"] verbs: ["create", "patch", "delete"] - apiGroups: [""] resources: ["pods/log"] verbs: ["get"]
- rbac.create : rbac을 생성한다. (create를 권장)
- rbac.resource : rbac으로 접근가능한 resource를 설정한다.
- rbac.verbs : rbac으로 resource에 대해 부여할 권한을 설정한다.
1
2
3
4
5
#############################################################################################
## WARNING: You enabled `rbac` without specifying if a service account should be created. ##
## Please set `serviceAccount.create` to either `true` or `false`. ##
## For backwards compatibility a service account will be created. ##
#############################################################################################
- 위와 같은 경고가 뜬다면, 아래와 같이
values.yaml파일에 추가1 2
serviceAccount: create: true
- 이미 존재하는 서비스 계정을 사용하려면 아래의 명령어를 사용 (아래 Kubernetes RBAC 설정 설명 참고)
1 2 3
rbac: create: false serviceAccountName: your-service-account
helm 설치하기(values.yaml 파일이 있는 폴더에서 아래 명령어를 수행)
1
helm install --namespace hello-world gitlab-runner -f values.yaml gitlab/gitlab-runner
Helm Chart를 사용하여 GitLab Runner 업그레이드
- GitLab 러너를 업그레이드하기 전에, GitLab에 러너를 중지시키고 모든 Job이 끝났는지 확인
- 러너를 중지시키는 것은 완료 시 권한부여 오류같이 Job에서 발생하는 문제를 방지할 수 있다.
1
helm upgrade --namespace <NAMESPACE> -f <CONFIG_VALUES_FILE> <RELEASE-NAME> gitlab/gitlab-runner
<NAMESPACE>는 GitLab 러너를 설치하기 원하는 Kubernetes Namespace<CONFIG_VALUES_FILE>은 커스텀 설정이 포함된 파일의 경로. Helm Chart를 사용하여 GitLab Runner 설정하기를 참고<RELEASE-NMAE>은 차트를 설치할 때 지어주는 이름. Helm Chart를 사용하여 GitLab Runner 설치하기에서는 gitlab-runner라고 했다.
GitLab Runner Helm Chart를 최신 버전이 아닌 특정 버전으로 업데이트하길 원한다면, helm upgrade 명령어에 –version
을 추가
Kubernetes RBAC 설정
- 특정 Namespace에 Runner를 사용하기 위해서는 몇 가지 설정이 필요
Namespace 생성
- Namespace의 경우 그룹이나 팀, 혹은 파트별로 구성
- 예시: group-a, group-b, team-a, team-b, part-a, part-b, dep-a, dep-b
- 아래 명령어를 실행하여 hello-world라는 Namespace를 생성
1
kubectl create namespace hello-world
- 생성된 Namespace 확인
1
kubectl get namespaces
- 생성된 Namespace로 이동(kubens가 설치되지 않았을 때 get 명령어에 -n 옵션으로 네임스페이스를 지정하면 된다.)
1
kubens hello-world
Service Account 생성
- Namespace를 관리할 Service Account 생성하여 관리
- 예시: sa-group-a, sa-group-b, sa-team-a, sa-team-b
- 아래 명령어를 실행하여 hello-sa라는 이름의 Service Account 생성
- namespace를 지정(예시는 hello-world namespace를 연결)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f - apiVersion: v1 kind: ServiceAccount metadata: name: hello-sa namespace: hello-world EOF
- namespace를 지정(예시는 hello-world namespace를 연결)
- Service Account 정보 확인
1
kubectl get serviceaccounts hello-sa -o yaml
Role 생성
hello-role이라는 이름의 Role을 생성1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f - apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: Role metadata: namespace: hello-world name: hello-role rules: - apiGroups: ["extensions", "apps"] resources: ["deployments"] verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch", "delete"] - apiGroups: [""] resources: ["pods","services","secrets","pods/exec", "serviceaccounts"] verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch", "delete"] EOF
Role 정보 확인
1
kubectl get roles hello-role -o yaml
Role Binding 생성
hello-rb라는 이름의 Role Binding을 생성하여hello-saService Account와hello-roleRole을 바인딩1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f - apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: RoleBinding metadata: namespace: hello-world name: hello-rb subjects: - kind: ServiceAccount name: hello-sa namespace: hello-world roleRef: kind: Role name: hello-role apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io EOF
Role Binding 정보를 확인
1
kubectl get rolebindings hello-rb -o yaml
만약 gitlab-ci.yml 에서 runner의 tag 또는 name을 지정할 경우 helm의 values.yaml에서 tags 혹은 name에 값을 설정해주면 된다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
## Specify the tags associated with the runner. Comma-separated list of tags.
##
## ref: https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/ci/runners/configure_runners.html#use-tags-to-control-which-jobs-a-runner-can-run
##
tags: "my-runner"
## Specify the name for the runner.
##
# name: ""
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.